Research and Development Projects Adopted in FY2014
Development of third generation DNA/RNA heteroduplex oligonucleotide
Project Leader:Yokota Takanori
Professor, Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Tokyo Medical and Dental University

Two major types of oligonucleotide drugs for gene silencing, small interfering RNA (siRNA) and antisense oligonucleotide (ASO),
bind to RNA by base pairing in a sequence-specific manner and downregulate gene expression by inducing enzyme-dependent degradation of targeted RNA.
It has now been over a decade since the discoveries of RNA interference (RNAi) and siRNAs, but despite some promising clinical trial results pharmaceutical company remains cautious about the therapeutic potential of RNAi-based drugs.
Here we developed a DNA/RNA heteroduplex oligonucleotide (HDO) with a structure different from that of the conventional oligonucleotides for gene silencing,
double-stranded RNA of siRNA and single-stranded DNA of ASO. When the DNA strand was used as an ASO and the RNA strand was conjugated with α-tocopherol,
it achieved silencing ability about more than 20 times that of ASO alone and can amplify effect of any reported ASOs.
The enhanced silencing ability included HDO effects as well as delivery effect of α-tocopherol to the liver. Since the HDO has a specific intracellular processing machinery,
we think that HDO is a brand new type oligonucleotide drug.
Although delivery organ of HDO was still limited to the liver, we r recently developed modified structure of HDO with administration method,
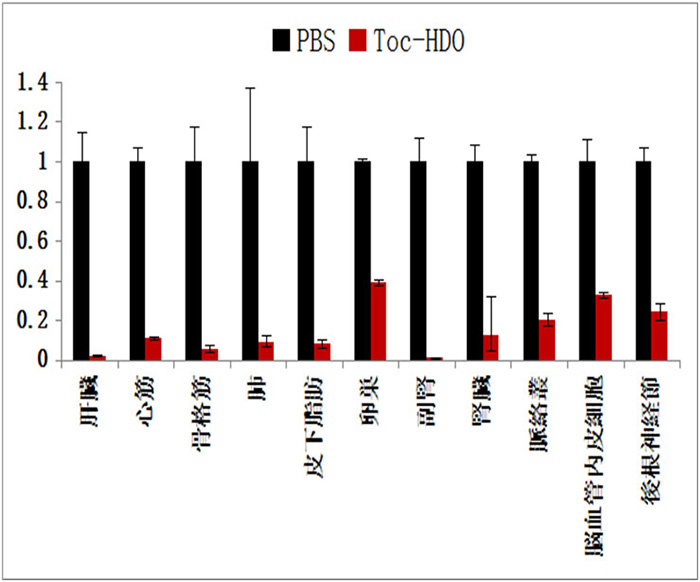
which can regulate many extra-hepatic organs, such as heart, kidney, spleen, lung, adrenal gland, subcutaneous adipose tissue and skeletal muscle as a second break of HDO.
This technology however has a considerable adverse effect of liver toxicity. In this project, we try to develop a sophisticate molecular design with negative targeting of liver and positive targeting to each extra-hepatic organs, and furthermore explore the new technology for oral and transdermal administration of HDO.

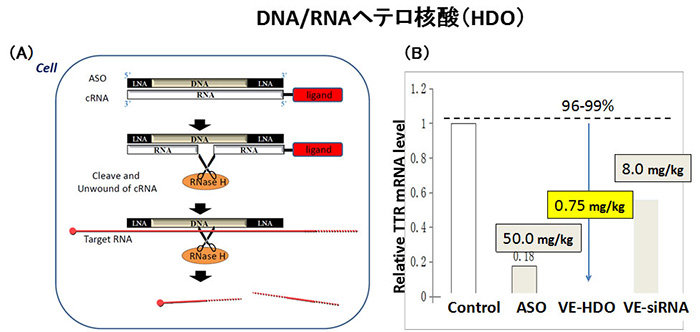
<Figure1>Gene suppression mechanism of DNA/RNA heteroduplex ologonucleotide (HDO)(A) and its in vivo efficacy (B)
(A)The HDO introduced by delivery ligand into a cell, complementary RNA (cRNA) is cleaved by RNase making parent antsense strand (ASO gapmer) fee and active,
and the ASO gapmer inhibit the target RNA RNase H-dependently. (B) The inhibition effect of HDO is much higher than ASO and siRNA in vivo.
<Figure2>
Intravenously-administered HDO suppresses the endogenous target genes in extra-hepatic many organs and tissues.