Research and Development Projects Adopted in FY2014
Smart chemobio antibodies design for unmet disease
Project Leader:Umetsu Mitsuo
Professor, Graduate School of Engineering, Tohoku University
In this project, we propose a novel medical molecular format which has effective activity for unmet disease by conjugating low molecular organic medicine with antibody fragments.
The medical molecules (we call 'chemobio antibodies') have both the benefit characters of low-molecular medicine and antibody: they can target as various molecules as low molecular organic medicine,
the function of low molecular organic medicine can be expressed, and further, they have as high specificity for target molecule and good clearance as antibody.
Recent analysis of human genome declared 1,500 ~ 2,000 molecules as medical targets, but the molecules targeted by low-molecular medicine and antibody are ~500 and 50, respectively:
more than half of targets has not been subjected to drug discovery because both the medical formats cannot express adequate function.
Low-molecular medicines can be designed for targeting various molecules present in and out of cells and they have various interaction with target molecules to express various function; however,
the affinity and specificity of low-molecular medicines is so low to lead to off-target reaction and side effect, and the low weight causes fast clearance. Whereas,
antibodies have high affinity for target molecules and its specificity leads to high accumulation on a specific tissue;
but the antibodies are not functional in cell and they only have the functions of neutralization and cell cytotoxicity such as ADCC and CDC.
Further, the large molecular weight of antibody (~15 k) hardly inserts into deep area of tissues.
Here, we conjugates the effective fragment of low-molecular medicine with antibody fragment to construct a medical molecule with novel structural format (chemobio antibody)
which has the same targeting capacity and functionality as low molecular organic medicine and further has the same affinity and specificity for targets as antibody. In this study,
we generate the chemobio antibody for kidney disease. The number of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients in Japan is ~ 580 million, but few medicine for CKD have been explored; consequently,
the medicines for other diseases such as antihypertensive drug and hyperlipemia are used.
Recently, some studies reported that PAI-1 overexpression accelerates CKD, and we have designed a low molecular molecule which can inhibit the activity of PAI-1.
Here, our interdisciplinary group consisting of protein engineer, synthetic chemist, pharmacologist, and medical scientist,
see the PAI-1 inhibitor and the antigen-binding fragments of the antibody with affinity for kidney cells as building-bricks to builds up the chemobio antibody for CKD from the bricks.
We will show the potential of the chemobio approach for designing the medicine for unmet disease.
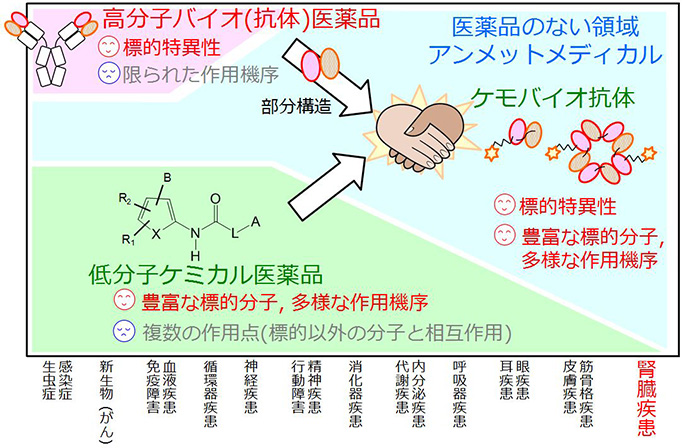
<Figure1>Unmet medical needs where small molecule medicine and antibody
Our study proposes the pharmaceutical format which can play an active part in unmet domain. Low-molecular medicines are intends for abundant target molecules,
and there is an advantage with a variety of action mechanism, but the specificity of low-molecular medicines is so low to lead to off-target reaction..
On the other hand, antibody medicine which is a biopharmaceutical representative has superior target specificity, but the action is limited to neutralization activity and cell cell cytotoxicity.
Therefore, we fuse the advantage structures of low-molecular medicine and antibody medicine to generate the scamobio antibody having both advantages,
and we apply kidney disease as a model for proposing a process of highly functionalizing low-molecular medicine by the use of the bio molecular structure.
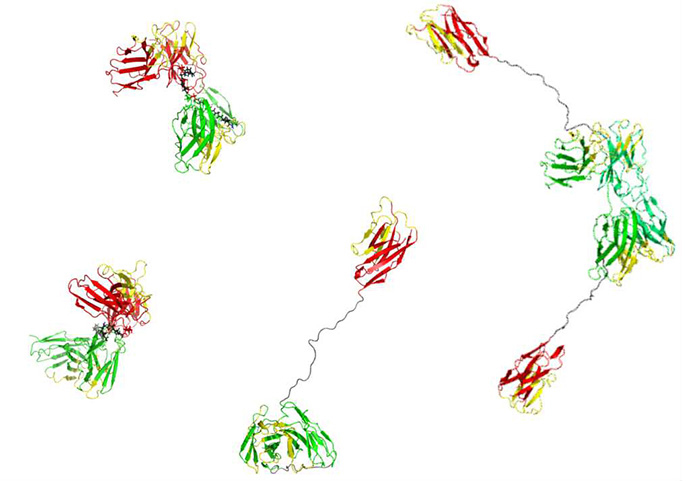
<Figure2>Various small molecule antibodies consisting of the variable region of the antibody
Various small molecule antibodies consisting of the variable region of the antibody:
We design the small molecule antibody with comparable affinity to IgG type antibody and without the Fc domain that worsens renal disease.
The small molecular antibodies are used for carrying PAI-1 inhibitor to the kidney organization.
<Figure3>Experiment scenery of the laboratory
<Figure4>Member photograph of the laboratory