<Figure1>
Status and issues on development of glycoprotein products, and research organization
HOME > Research and Development Projects Adopted in FY2015 > Development of a glycosylation analysis and control system to manufacture functionalized glycoprotein products
Project Leader:Kawasaki Nana
Professor, Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University
Many glycoproteins have been approved for clinical use. Carbohydrate moieties in biopharmaceuticals are highly heterogeneous and can be altered depending on the variations in the manufacturing processes (such as difference in the scales used, cultivating conditions, and purification methods). Changes in the carbohydrate heterogeneity possibly affect their in vivo activity, circulating half-life, immunogenicity, and physicochemical properties, and can consequently have harmful impacts on the efficacy and safety of the pharmaceuticals. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the carbohydrate structures and their impacts on the quality, efficacy and safety of the drug, and subsequently to mantain an appropriate glycan profile to ensure the target quality, efficacy and safety of the pharmaceuticals (glycan functionalization). Mostly, the functionalization is achieved by optimization of the process parameters, materials, and various tests.
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a frequently used method for the structural analysis of glycoproteins. Appropriate knowledge and experiments are required to analyze highly complex and diverse glycoproteins using MS. Optimization of the several parameters that affect carbohydrate heterogeneity are not only expensive but also time consuming. Thus, manufacturers desire the system which enables automated and rapid glycan structural analysis, quantification, optimization of process parameters, and control of glycan-related processes to manufacture glycoprotein products.
In this study, Yokohama City University, Mitsui knowledge industry and Thermo Fisher Scientific develop the glycosylation analysis and control system, including LC/MS and an algorism for structural and quantitative analysis of N-glycosylation on the glycoproteins. Using small scale single use perfusion system, the Kihara Memorial Yokohama Foundation experimentally produces mAbs bearing various glycans for developing the system. The foundation also evaluates the feasibility of the system for manufacturing mAb products at a large scale. The success of our project will provide a glycosylation-controllable manufacturing system, and it will facilitate a development of both innovative and biosimilar glycoprotein products.

Status and issues on development of glycoprotein products, and research organization
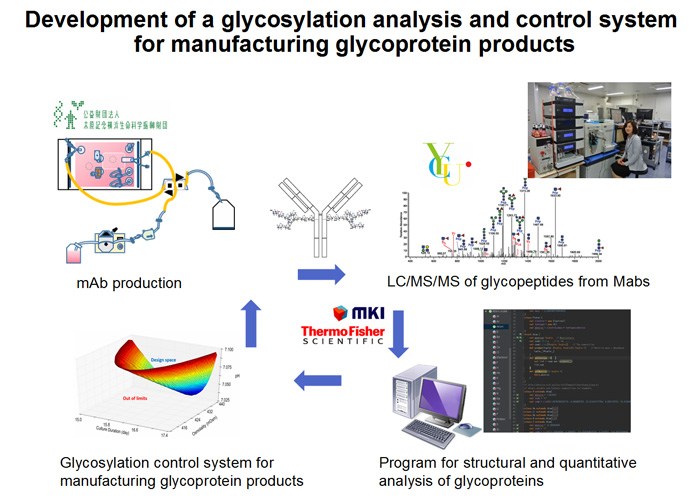
Strategy for the development of the glycosylation analysis and control system for glycoprotein products
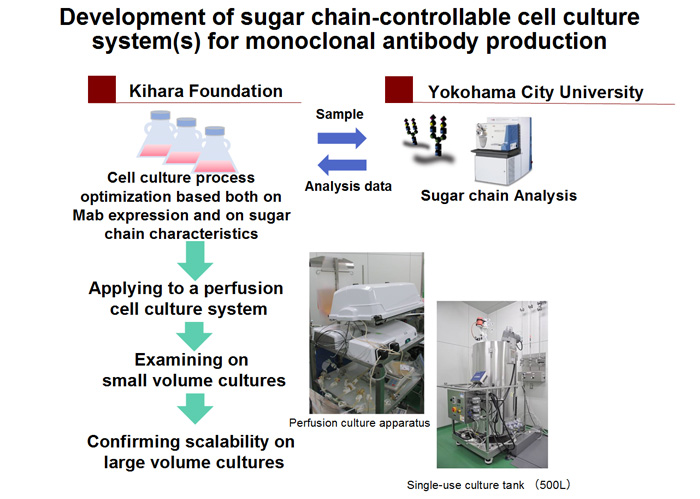
Strategy for the development of sugar chain –controllable cell culture system(s) for monoclonal antibody production

Project members, Yokohama City University and Kihara Memorial Yokohama Foundation, in front of the GMP facility in the Kihara Memorial Yokohama Foundation