Division of Biobank
List of our News
-
03/31/20Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization and Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association launched a joint research project aiming at the early practical application of preventive/preemptive medical solutions
-
03/26/20Elucidation of regional diversity in a Japanese population using machine learning for large-scale genomics - Utilization of Japanese genome data for genomic personalized medicine -
-
03/25/20Publication of primate omics database, D3G, for drug discovery - Provision of high-quality data, including human and non-human primate genomes -
-
03/24/20Hypertension and obesity were identified as major risk factors for shortening the life spans of today using genomic information collected from 700,000 people - Elucidation of health factors, treatable in all people, using inherent genetic information -
-
03/06/20Characterization of mitochondria carrying unique genomes in a Japanese population
-
02/26/20Discovery of novel treatment target and predictive markers of postoperative prognosis for lung cancer frequently observed in the Japanese (lung adenocarcinoma)
-
02/04/20Establishment of a genetic risk score model for ischemic stroke: Validation in a prospective cohort in the “Hisayama Study”
-
01/20/20Identification of gene regions and traits responsible for adaptive evolution in Japanese and Westerners - Alcohol and bread intakes are deeply involved in Japanese and Westerners, respectively
-
12/05/19Discovering genetic variations for genomic studies in populations across Asia: Whole-genome sequencing of over 200 population groups in 64 countries
-
10/28/19Commencement of the Biobank cross-search System, where 650,000 samples and/or 200,000 data owned by seven Biobank institutes in Japan can be accessed at once
Profile of the Division of Biobank
In light of the rapid progress in analysis technology at the genomic level, the Division of Biobank strives to strengthen the foundation of genome analysis while encouraging R&D to clarify how genetic and environmental factors relate to specific diseases and promote clinical applications of the findings with the aim of swiftly returning to the public the benefits of the clarification.
Specifically, while working to establish a biobank for specimens of diseases and healthy donors, the department analyzes such data as genome analysis information and clinical information to identify and verify the genes related to the onset of diseases and drug responsiveness and to identify the standard genome sequence of Japanese people. In addition, through collaborative and ancillary genome research, the department not only aims to track down the causal genes of rare/intractable diseases, but also to contribute to the formulation of innovative diagnostic/treatment guidelines based on genome information. Furthermore, the department is pushing forward experimental/empirical clinical research to strengthen the research foundation and establish a system for offering genomic medical care toward the goal of turning genomic medicine into reality.
Through these initiatives, the department aims to achieve the following by 2020.
- To find evidence associated with risk prediction/prevention, diagnosis (stratification), treatment, and drug selection/optimization for diabetes and other diseases
- To commence clinical research associated with predictive cancer diagnostics and treatment responses to anticancer and other drugs, and prediction of their side effects
- To commence clinical research associated with genomic medicine in the fields of dementia and sensory systems
- To commence clinical research associated with innovative methods of diagnosis and treatment for intractable neuromuscular diseases
Under AMED's Japan Genomic Medicine Project, the Data-sharing Policy for the Realization of Genomic Medicine was formulated to clarify the policy to be followed with respect to the sharing of genome information with the aim of promoting data sharing in related fields.
Furthermore, under the National BioResource Project, bioresources such as experimental animals, plants and micro-organisms that are of fundamental importance in life science research and critical for the nation to strategically organize are systematically collected, preserved and provided. In addition, with the aim of enhancing the quality of bioresources, efforts are made to secure bioresources that meet the needs of the time by developing preservation technologies and adding more value to them by way of genome analysis.
Contact:
Division of Biobank, AMED
TEL: +81-3-6870-2228
Email: kiban-kenkyu”AT”amed.go.jp
Data Sharing Policy
AMED has drawn up Data sharing Policy for the Realization of Genomic Medicine that guides sharing of genomic information, and made data sharing obligatory for R&D projects which are in scope of the policy as a general rule. With the objective of practicing prompt, extensive and appropriate disclosure and sharing of genome data associated with research outcomes and genome information including clinical information and analysis/interpretation results, the Policy defines a framework for protecting the rights of research participants and researchers who provided the data and information, while, at the same time, facilitating research in related fields through data sharing.
Data and its sharing database- Open Data:NBDC Human Database
 MGeND
MGeND 
- Controlled-Access Data:NBDC Human Database

- Group Sharing Data:AGD
 (Japanese Only)
(Japanese Only)
Overviews of the data produced by R&D projects which are in scope of the policy are here  (Japanese only).
(Japanese only).
GEM Japan
The GEM Japan (GEnome Medicine Alliance Japan), whose purpose is to integrate the results of AMED projects toward the realization of genomic medicine in Japan, was designated as a GA4GH Driver Project.
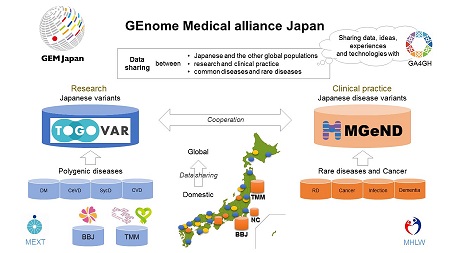
- About GEM Japan

